Getting Started
VoiceCulture is built with flexibility and editor tooling in mind. To get started, you'll need to configure the project-level and editor-level settings through Unreal's Developer Settings system.
1. Voice Culture Settings (Project)
The main configuration for runtime behavior is handled via the USSVoiceCultureSettings class, accessible through Project Settings > Voice Culture.
This is where you define the supported cultures, default fallback, and runtime culture preferences.
Available Properties
-
DefaultLanguageFallback
The fallback culture to use when a localized voice is missing.
Example:"en" -
CurrentLanguage
The current runtime language. Used to resolve which voice line to play. This can be updated at runtime (e.g., via UI or platform settings). -
SupportedVoiceCultures
A set of culture codes (e.g.,"en","fr","ja") representing the languages supported by your game. -
bUsePreviewLanguageInGame
If enabled, the preview language (set below) will be used in PIE (Play In Editor) and runtime simulation. Useful for development testing. -
PreviewLanguage
The culture code used for previewing during development if the above option is enabled.
Example
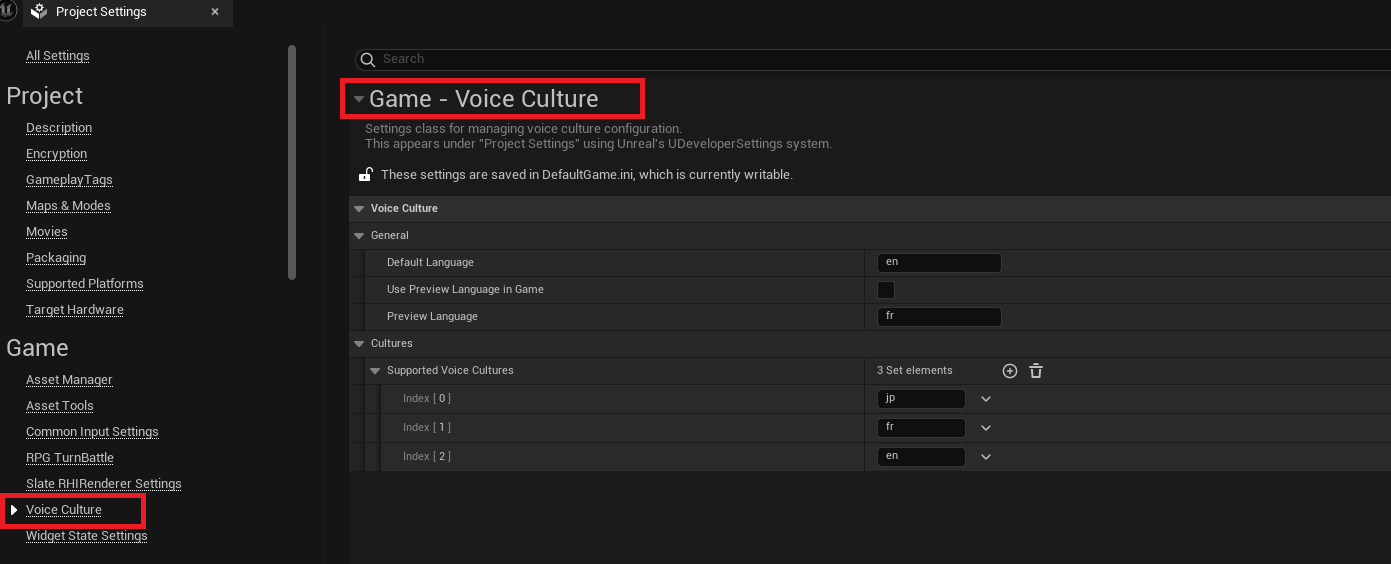
[/Script/SSVoiceCulture.SSVoiceCultureSettings]
DefaultLanguage=en
bUsePreviewLanguageInGame=False
PreviewLanguage=fr
+SupportedVoiceCultures=en
+SupportedVoiceCultures=fr
+SupportedVoiceCultures=jp
2. Editor Settings (Per-User)
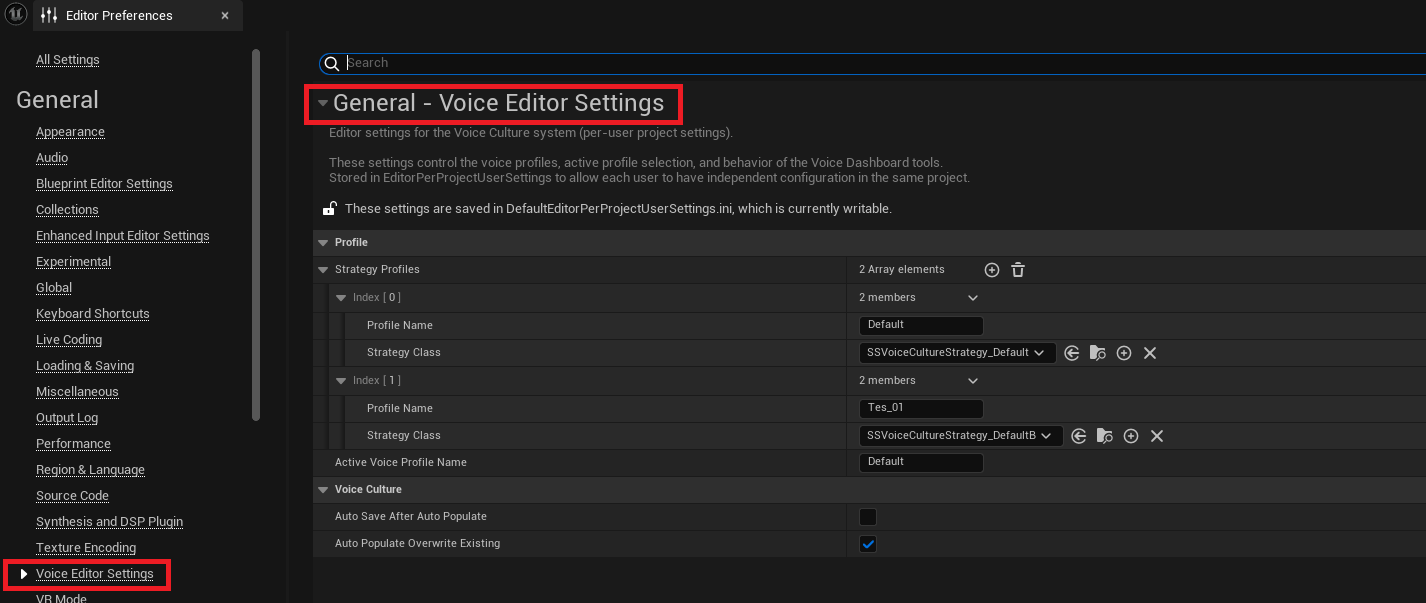
The editor-specific configuration is handled by USSVoiceCultureEditorSettings, available under Editor Preferences > Voice Editor Settings.
These settings are stored per user, allowing each team member to have independent configurations for workflows like auto-population and strategy profiles.
Available Properties
-
StrategyProfiles
A list of custom profiles defining how voice assets are filtered, categorized, or named. Useful for tooling or batch imports. -
ActiveVoiceProfileName
The name of the currently active profile from the list above. -
FallbackProfile
A default profile used in case the active profile is invalid or missing. -
bAutoSaveAfterAutoPopulate
If enabled, the system will save voice assets automatically after a bulk operation (like auto-populate). Great for reducing manual steps. -
bAutoPopulateOverwriteExisting
Allows overwriting existing voice data when auto-populating assets.
3. Accessing the Settings in Code
You can access the project-level settings statically from anywhere in your code:
const USSVoiceCultureSettings* Settings = USSVoiceCultureSettings::GetSetting();
FString CurrentLang = Settings->GetCurrentLanguage();
To get the editor settings (for use in tools or custom editor workflows):
const USSVoiceCultureEditorSettings* EditorSettings = USSVoiceCultureEditorSettings::GetSetting();
If you need to modify the settings during runtime or editor scripts, use the mutable versions:
USSVoiceCultureSettings* MutableSettings = USSVoiceCultureSettings::GetMutableSetting();
MutableSettings->CurrentLanguage = TEXT("ja");
MutableSettings->SaveConfig();